In order to execute the Read RDBMS Table examples these three components must be set-up. They are:
1. The SQLAlchemy Library
2. The appropriate RDBMS driver library, in our case, the pyodbc library
3. The appropriately configured Windows ODBC client connecting to a target database
These instructions are specific to Microsoft SQL Server 2017 for Windows 10.
SQLAlchemy Library
To confirm a version of the SQLAlchemy library is available start a Python session and enter:
import sqlalchemy
sqlalchemy.__version__
'1.2.7'
Notice the two consecutive underscores before and after the string version.
pyodbc Library
Confirm the pyodbc library is available.
import pyodbc
pyodbc.version
'4.0.23'
SQL/Server configuration
Our set-up has both Python 3.6 and SQL Server 2017 executing on the same Windows 10 machine. If the SQL Server instance is running remotely you will need to make the appropriate adjustments.
Configure an ODBC DSN to connect to the target RDBMS. Set-up the ODBC client interface on Windows 10 by launching the ODBC Data Source Administrator by clicking the Windows Start Menu:
Start -> Windows Administrative Tools -> ODBC Data Sources (64 bit) to launch the ODBC Data Source Administrator.

If you are using Windows 7 navigate to Control Panel -> System and Security -> Administrative Tools and select Data Sources (ODBC). These examples illustrate the ODBC set-up for Windows 10.
Make sure that the System DSN tab is selected and then click the Add… button to select the driver for the SQL Server Database.

Press the Finish button which displays the Create a New Data Source to SQL Server dialog box
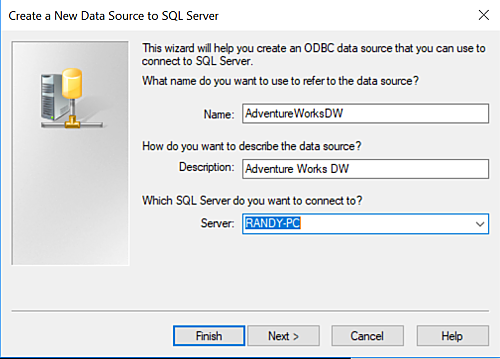
For Name: we choose AdventureWorksDW to indicate we are using the AdventureWorksDW2017 database SQL Server ships as an illustration for their Analytical Services.
For Server: supply the instance name of the SQL Server database to connect to. In our case the SQL Server instance name is a local instance named RANDY-PC. We use AdventureWorksDW as the name for ODBC source name which in turn connects to the SQL Server AdventureWorksDW2017 database.
More information about the AdventureWorks2017 sample databases is here.
Press the Next> dialog box.
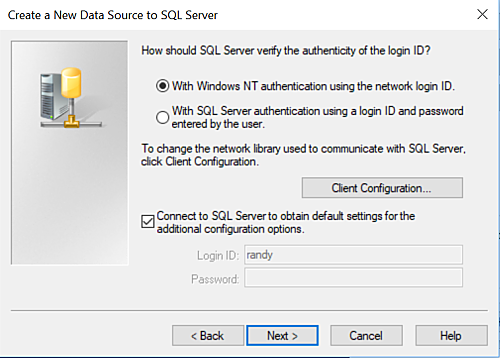
In our case we select Windows NT authetication using the network login ID. Press the Next> dialog box. This action presents the Change Default Database dialog menu.
If the dialog box indicates master as the default database then check the box labeled Change the defauly database to: and select AdventureWorksDW2017 assuming it is available and your account has been granted read access.

Check the Change the default database tick box and supply the database name AdventureWorksDW2017.
Press Next> button to be presented with the Change the language of SQL Server message to: dialog box. In our case we chose to log the ODBC driver statistics.
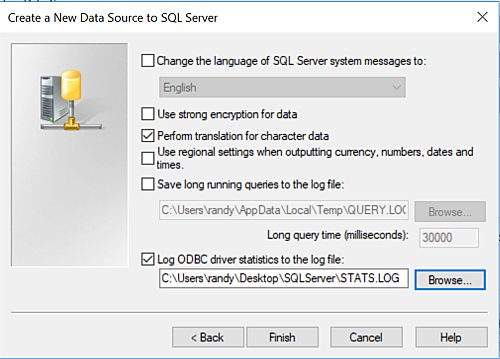
Press Next> to be presented with the ODBC Data Source Configuration panel.

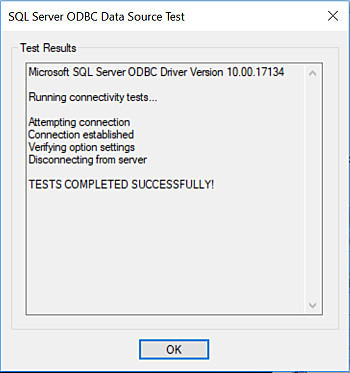
Press the Test Data Source> box to test the ODBC connection. You should see the Test Results dialogue box shown.
To connect to the SQL Server AdventureWorksDW2017 database with SQLAlchemy use the create_engine function to create an engine object from the database URI.
You need only create the engine once per database instance to which you are connecting.
Illustrate the create_engine function containing the SQL Server Database URI.
import pyodbc
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, MetaData, Table, select
ServerName = "RANDY-PC"
Database = "AdventureWorksDW2017?driver=SQL+Server"
TableName = "DimCustomer"
engine = create_engine('mssql+pyodbc://' + ServerName + '/' + Database)
print(engine)
Engine(mssql+pyodbc://RANDY-PC/AdventureWorksDW2017?driver=SQL Server)
In cases where the SQL Server instance is remote to the Python session the engine object string will be similar to:
mssql+pyodbc://USER:PW@SERVER/AdventureWorksDW?driver=ODBC+Driver+13+for+SQL+Server
where USER:PW are the userid and password pair and SERVER is the remote hostname or IP address running the SQL Server instances. The ODBC driver name could be different depending on which driver you use. You may need to contact database administrator for additional information.